
Measuring Z0 using reflection coefficient Only one solution (so far) is capable of measuring Z0 over frequency such that dispersion can be observed. About the only thing they have in common is they all use electrical measurements of transmission lines, as opposed to electromagnetic or closed-form simulations. This page will tie together some different attempts of measuring characteristic impedance (Z0). Finally, verify your design by calculating or measuring the S-parameters of your matching network and check if they meet your specifications.Click here to go to our main measurement pageĬlick here to go to our page on characteristic impedanceĬlick here to go to our time domain reflectometry pageĬlick here to go to our page on quarter-wave transformers There are various methods like constant resistance circles, constant reactance circles, or constant VSWR circles that can help you find an optimal path and component values.
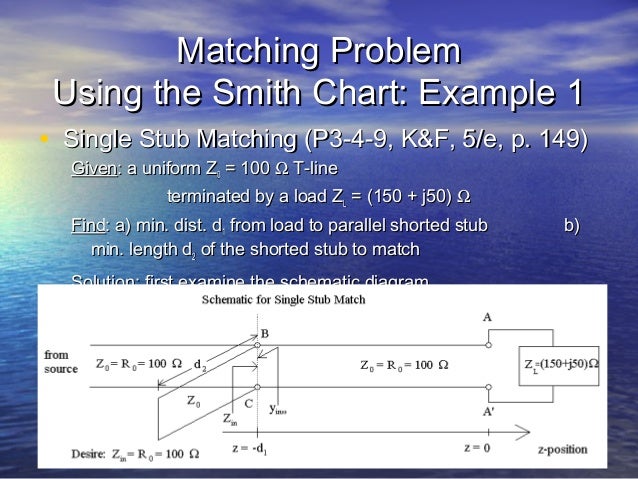
After selecting a matching network topology, such as a series or parallel L-network, a pi-network, or a T-network - each with their own advantages and disadvantages - use the Smith chart to find the values of the components that will transform the load impedance to the source impedance along a path on the chart. Then plot the normalized load impedance on the Smith chart and locate the point that corresponds to the normalized source impedance - this is your target match. To use Smith charts for designing matching networks, you must first determine the impedance of your source and load at the operating frequency, and normalize them to the characteristic impedance of your transmission line.
Matching networks can be composed of passive components, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, or active components, such as transistors and amplifiers.
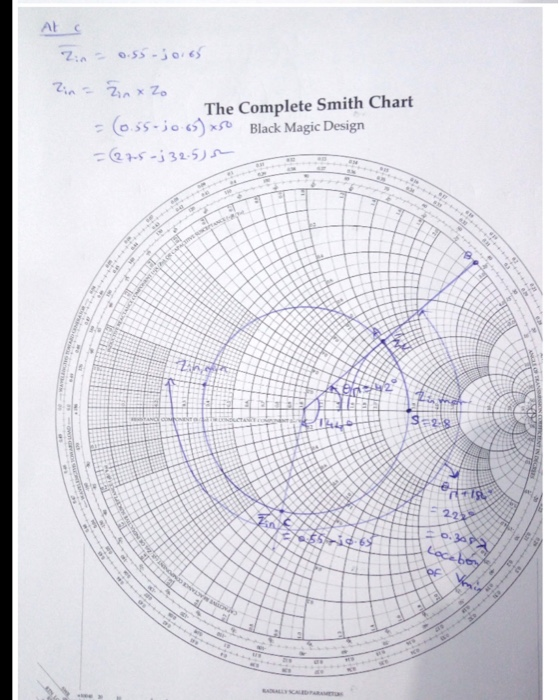
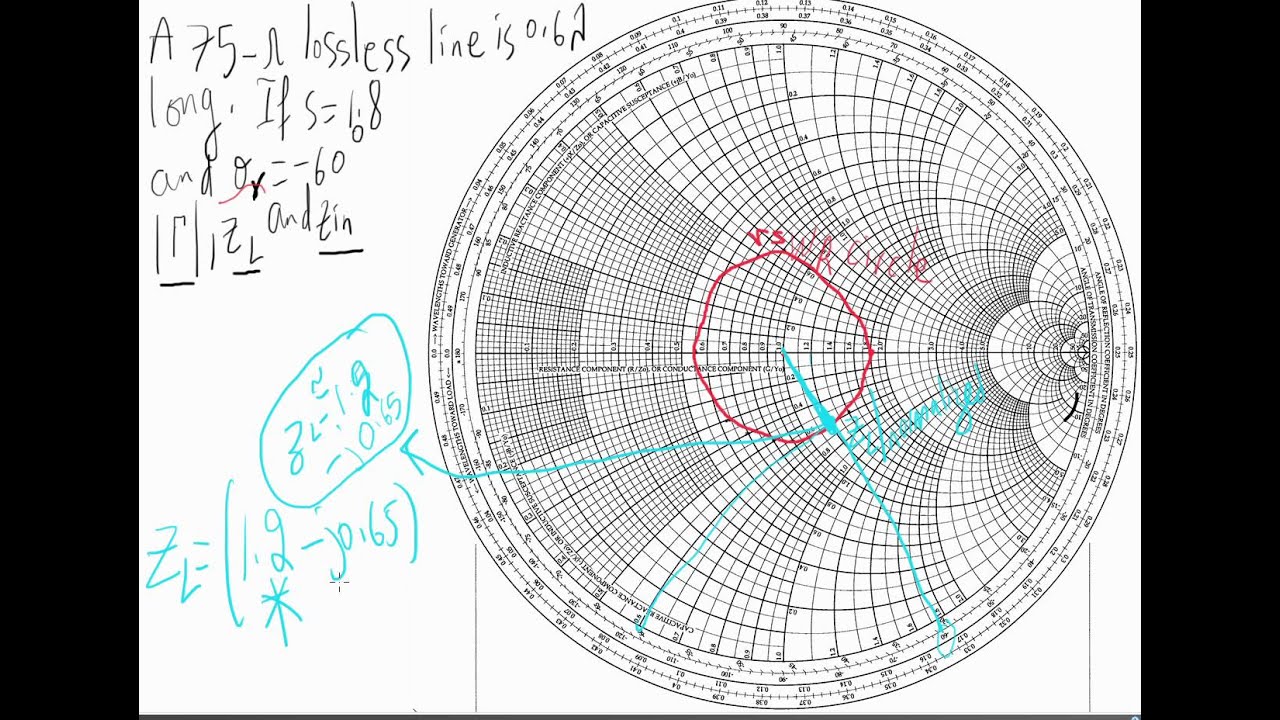
One of the applications of Smith charts is to design matching networks, which are circuits that modify the impedance of a load to match the impedance of a source.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
